

News
 电商部
电商部  2026-01-21 10:20:38
2026-01-21 10:20:38 Industrial-grade Memory Card vs. Consumer-grade: Key Differences You Must Know
Industrial-grade memory cards and consumer-grade ones may look identical in appearance, sharing the same standard interfaces that allow them to fit into most device slots. However, their core performances, design philosophies, and application scenarios are vastly different. This fundamental gap determines their respective boundaries of use—consumer-grade cards are designed for civilian scenarios like smartphones, cameras, and USB drives, prioritizing cost-effectiveness and portability. In contrast, industrial-grade memory cards focus on stability, durability, and data security, making them irreplaceable in critical industrial environments such as industrial automation, rail transit, and energy monitoring.
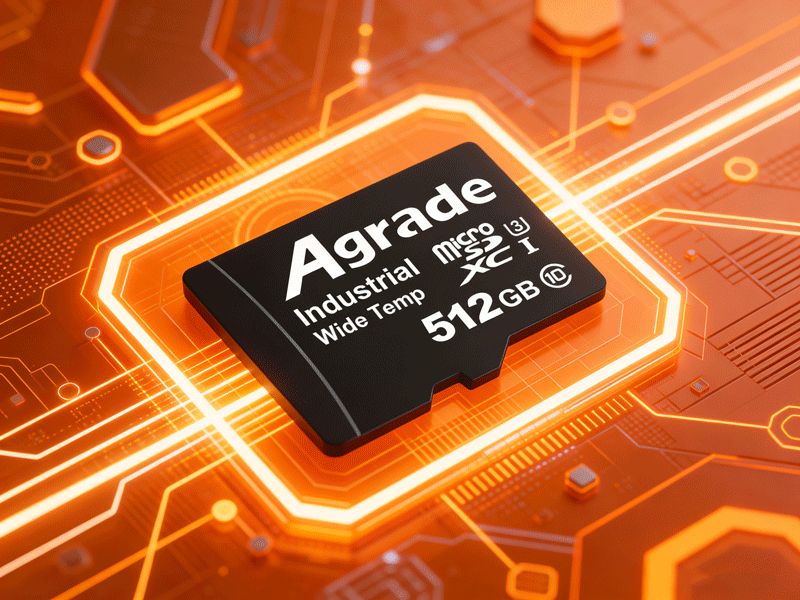
The most intuitive difference lies in environmental adaptability. Consumer-grade cards are tailored for indoor room temperature environments, with an operating temperature range of only 0℃ to 70℃. They lack designs for shock resistance, dustproofing, and moistureproofing, making them prone to performance degradation in extreme conditions like outdoor low temperatures, high-temperature factory workshops, and humid environments. Industrial-grade memory cards, however, are optimized for harsh environments, generally supporting a wide temperature range of -40℃ to 85℃. Some high-end models can even extend to -55℃ to 105℃, easily coping with extreme temperatures such as cold winters outdoors, scorching heat in deserts, and low temperatures in cold storage.
Durability is another crucial distinction that directly affects service life. To control costs, consumer-grade cards mostly use TLC NAND flash memory, with a P/E (Program/Erase) cycle count of only 3,000 to 10,000 times and a TBW (Total Bytes Written) generally below 10TB. They cannot withstand the 24/7 high-intensity writing demands of industrial equipment, and are prone to speed degradation and increasing bad blocks after long-term use. Industrial-grade cards, on the other hand, prioritize SLC or MLC flash memory. SLC versions offer a P/E cycle count of over 100,000 times, while MLC versions can reach 10,000 to 30,000 times, with a TBW of generally ≥50TB and even hundreds of TB for high-end models.
Data security and stability are the core competitiveness of industrial-grade cards, advantages that consumer-grade cards cannot match. Equipped with advanced ECC (Error-Correcting Code) technology, industrial-grade cards can real-time detect and correct single-bit errors, and alert multi-bit errors, significantly reducing the risk of data corruption during transmission and storage. Most also feature power-fail protection, using built-in supercapacitors to reserve emergency power, ensuring cached data is completely written to flash memory when a sudden power outage occurs. After rigorous tests including high-low temperature cycles, vibration, and electromagnetic compatibility, their MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) exceeds 1 million hours, far surpassing the tens of thousands of hours of consumer-grade cards.



























































